3CO01 Assignment Example
- January 17, 2022
- Posted by: Assignment Help Gurus
- Category: CIPD LEVEL 3 CIPD CIPD EXAMPLES HUMAN RESOURCE
Table of Contents
3CO01 Business Culture and Change in Context

Case study
You work in the HR Team of a medium sized organisation and are studying for your people practice qualification. In a recent discussion with your manager, you expressed how important you thought it was for employees to understand the business environment. You feel this is especially important for people practice professionals as their roles impact on the policies, processes and values of the organisation, which in turn impact on all the people within the organisation.
Inspired by this discussion, your manager has asked you to help prepare
development day. A team-based learning needs analysis has shown that as well as more knowledge about the business environment, the team would benefit from a deeper understanding of organisational culture and how humans behave in organisations. The team would also like to build their knowledge and skills in relation to change management.
Preparation for the Tasks:
- At the start of your assignment, you are encouraged to plan your assessment work with your Assessor, and, where appropriate, agree milestones, so that they can help you monitor your progress.
- Refer to the indicative content in the unit to guide and support your evidence.
- Pay attention to how your evidence is presented, remember you are working in the People Practice Team.
- Ensure that the evidence generated for this assessment remains your own work.
You will also benefit from:
- Completing and acting on formative feedback from your Assessor.
- Reflecting on your own experiences of learning opportunities and continuing professional development.
- Reading the CIPD Insight, Fact Sheets and related online materials on these topics.
Task One-Slide Deck for Team Day
Your manager has asked you to prepare a presentation (slide deck and brief presenter notes) in readiness for delivery to the HR Team at the next Team day. The aim of the presentation, entitled
is for team members to gain a general understanding of their business environment and the key issues that can affect this.
Your presentation (which you are not required to deliver) can be based on your own organisation or one(s) that you are familiar with, and should include the following:
- Application of an analysis tool (such as PESTLE) to examine the key external forces impacting or likely to impact an ties. (AC 1.1)
- An explanation of business goals and why it is important for organisations to plan for how they will achieve these. Your explanation should include examples of planning, such as how a business has been structured or specific policies introduced or people practices followed, in order for business goals to be achieved. (AC 1.2)
- An explanation of an organisation s products and/or services and main customers. (AC 1.3)
- A short review of different technologies available to people professionals and how these can be used to improve working practices and collaboration. You might consider for example, technologies relating to communications, information sharing, record keeping, learning, wellbeing, productivity or security. (AC 1.4)
Task Two Guidance Leaflet
In line with the team learning need analysis and knowing that they will be required to support a number of change initiatives soon, your manager has also asked you to prepare a guidance leaflet for the team. The guidance leaflet should cover two main themes and include
- information about organisational culture and how people behave in organisations
- guidance about the impact of change and how organisational change can most effectivelybe managed.
Your guidance leaflet should explain (in any sequence):
- What is meant by workplace (organisation) culture (AC 2.1)
- Why it is important to foster an appropriate and effective workplace culture. (AC 2.1)
- How organisations are whole systems in which different areas and aspects such as structure, systems and culture, are all inter-related. (AC 2.2)
- An example of how good people practice, and an example of how bad people practice can impact other parts of the organisation or beyond the organisation (for example through developing new and better ways of doing things or through poor practice stimulating new legislation). (AC 2.2)
- How individuals may learn and develop in different ways in organisations and how this might be accommodated in assessing and developing skills and capabilities. (AC 2.3)
- Why it is important for an organisation that change is predicted, planned and effectively managed. (AC 3.1)
- How change can impact people in organisations, such as changing their role or status or financial situation, and the different ways people may respond to change. (AC 3.3)
- The nature and importance of different roles that can be played by people practice professionals, in relation to change agendas. You might consider roles such as: gatekeeper, champion, facilitator, critical friend or record-keeper. (AC 3.2)
Solution Task One
AC 1.1 Examine the key external influences that impact on business environments

Organisations do not operate in a vacuum rather their operations are influenced by external forces in their business worlds. To this end, there exists several tools that help in the analysis of external factors that affect business in all sectors including the hospitality industry that forms the core of our business. Among such tools is the PESTLE analysis that is an acronym for Political, Economic, Sociological, Technological, Legal and Environmental. Cipd (2021) defines the PESTLE analysis as a strategic, broad fact finding activity of the external factors that potentially influence the decisions of companies by assisting to minimise the threats and subsequently maximise on the available opportunities. The following is analysis of the factors within the hospitality industry
- Political factors that influence the industry include environmental regulations, tax policy, trade restrictions, political stability and tariffs. This has been evidence during the Covid19 pandemic period as many governments imposed travel bans that negatively affected the industry Frue (2019). Similarly, the hospitality industry operates in fear during presidential elections as new governments could introduce new ideas and policies that impact on the industry and disrupts the operations.
- Economic factors that influence the industry include economic growth or decline, inflation, interest, wage rates, exchange rate, minimum wage, working hours, cost of living, availability of credit and unemployment. In this regard, the strength or weakness if a currency can affect the attractiveness of a vacation destination. The short term impact of Brexit was loss of a substantial number of employees from other EU countries (James, 2021).
- Sociological factors include cultural norms, health consciousness, career attitudes, age distribution population growth rates, health and safety. For example, consumers have become more health conscious during the Covid19 pandemic period and hence the industry investment on sanitising procedures for their facilities.
- Technological factors include new technologies for example robotics and rate of change (Cipd, 2021). To this end, some hotels have adopted robotics in sanitising their facilities which is faster and more efficient. The industry is also investing in social media and working towards getting positive reviews on travelling websites ( Frue, 2019)
- Legal factors include changes to legislations such as employment, imports/exports, access to quotas, materials and taxation (Cipd, 2021)
- Environmental factors include ethical sourcing, global warming, pandemics and other emergencies. Frue (2019) noted that the industry have to understand the seasonal or weather differences to competitively price their rooms.
AC 2.1 Discuss organisational goals and why it is important for organisations to plan.

According to Hill (2019) planning is a process that charts a course for attainment of defined business goals. The process entails conducting a review of operations of the organisation and subsequently identifying what needs to be improved in the next year. As such planning necessitates forecasting of the results that an organisation desires to achieve and identifying the measures to be taken in order to attain the set goals. The results can be can be in financial terms or other measures such as consumer satisfaction (Hill, 2019).
Scott (2010) explained that human resources personnel have different functions in organisations including ensuring that there policies put in place to ensure that employees are responsible for the attainment of organisational objectives and goals. Giving reference to the hospitality industry, it is broadly structured into food and beverages, travel and tourism, lodging and recreation (Novak, 2017). Their ultimate goal is to create a positive customer experience so as retain the consumer in future or even gain a referral.
In line with this, the HR department training and development plans within the hospitality industry seeks to invest in imparting the right knowledge and skills to the employees who are the direct link between an organisation and the company. Scott (2010) detailed that HR professionals are charged with responsibility of developing training and development programs that strengthen the quality of work in a company. This proceed upon evaluating the training needs, developing manuals, facilitating instruction and ascertaining that training objectives align to the business goals. Scott (2010) highlight the findings of the Bureau of Labor statistics denoting that imparting employees with skills can enhance organisational performance and help achieve business results.
AC 1.3 Discuss the products and/or services the organisation delivers, including who the main customers are

Bansal, Gaulum, Anbardar and Kumar (n.d.) cited Philip Kotler’s definition of a product as a bundle of a physical service and symbolic particulars that are anticipated to be beneficial to the buyer or yield satisfaction to a consumer.
The hospitality industry has five components of hospitality products including core products that refers to the basic benefit accorded to a guest such as a place to eat. The second is facilitating products that refers to those products that are provided to a guest in order to utilise the core product such as food in case of restaurants. Consequently, there are tangible products that refer to physical products of hospitality such as television and air conditioning in a standard room. There are supporting products that are provided to increase the value of the basic product with the intention of making it unique. Last but not least are augmented products refers to the products that are essential in enhancing the quality of products devoid of additional charges.
On the other hand, Bansal et al. (n.d.) defined services as the intangible activities that provide want satisfaction. It is also defined as any activity that one party offers to another and does not yield to ownership. Services can also be articulated as intangible economic products that involves human beings serving the provider and the recipient. They have several traits such as they are perishable, they lack physical identity, they are inseparable, have high fixed costs and are interdependent.
Capozzi (2020) argued that consumers in the hospitality industry can be categorised into backpackers and solo travellers that enjoy exploring cities and spending time in hotels and thus choose low prices over services and amenities. The other category is couples that involves romantic partners seeking quiet premises and high quality bedding. The other group is families that have more specific needs such as on site play areas, discounts for kids’ rooms, entertainment and additional amenities such as booster chairs. Business travellers is the final category and requires fast internet access, electronics such as printers and are usually willing to pay a higher price for rooms.
AC 1.4 Review the range of technology available within the people profession, including how it can be utilised to improve working practices and collaboration

As the world and the workplace become increasingly digitised HR managers are also forced to adapt to new technology that has enhanced their work. Technology is utilised in managing information on the cloud, engaging with people on social media sites and working on the go through tablets and mobiles (Barcelos, 2018).the following are some of the technology pieces required by people professionals
- Social media platforms such as Facebook, twitter and LinkedIn and are used for posting vacant positions, communicate on upcoming events to the public and helps in making decisions on the right fit for a company
- Human Resources Information Software (HRIS) helps in streamlining several HR processes and tasks that diminish manual errors. Besides automating HR functions it also helps in easier management of HR documents
- Cloud technology that assists in centralisation of business and HR data from payroll to feedback, enhances transparency within the organisation and boosts consistency.
- Gamification techniques that are utilised in recruitment to enhance talent acquisition. It is also used to enhance learning and development through knowledge sharing and simulation of real life contexts.
(Adapted from Bercelos, 2018).
Bibliography
Barcelos, K. (2018). Top 6 Technology Skills Every HR Professional Needs Today. [online] AIHR. Available at: https://www.aihr.com/blog/technology-skills-every-hr-professional-needs/.
Capozzi, C. (2020). Service Marketing vs. Product Marketing in Hotels. [online] Small Business – Chron.com. Available at: https://smallbusiness.chron.com/service-marketing-vs-product-marketing-hotels-23637.html.
Frue, K. (2019). PESTLE Analysis for Hotel Industry. [online] PESTLE Analysis. Available at: https://pestleanalysis.com/pestle-analysis-for-hotel-industry/.
Hill, B. (2019). How to Analyze the Key Success Factors for Plan Implementation. [online] Small Business – Chron.com. Available at: https://smallbusiness.chron.com/analyze-key-success-factors-plan-implementation-47365.html.
James, W. (2021). The impact of Brexit on the hospitality sector; what’s the post-Brexit outlook? [online] Stint. Available at: https://stint.co/learning-hub/the-impact-of-brexit-on-the-hospitality-sector/.
Novak, P. (2017). What Are The 4 Segments Of The Hospitality Industry. [online] Hospitality Net. Available at: https://www.hospitalitynet.org/opinion/4082318.html.
Scott, S. (2010). Role of HR in Achieving Business Goals. [online] Chron.com. Available at: https://smallbusiness.chron.com/role-hr-achieving-business-goals-1767.html.
Solution Task Two
AC 2.1 Define workplace culture in organisational settings and the importance of fostering positive approaches towards it.
Workplace culture in organisations can be defined as the set of underlying beliefs, principles and values that serve as the cornerstone of a company’s management system. It is also inclusive of the management behaviours and practices adopted in reinforcing the basic beliefs (Cipd, 2020). Tarver (2021) defined corporate culture as the beliefs and behaviours that guide how employees and the management interact and conduct business transactions. Tarver (2021) emphasized that corporate culture though not expressly defined it is implied and organically develops over time as an organisation hires people that represent it. The culture at the workplace is demonstrated by business hours, hiring decisions, dress code, and treatment of consumers, office set up, consumer satisfaction, employee benefits and turnover.
Workplace culture offers employee a way to understand the company, develop a network and common purpose as well as voice their views in reference to the mission of the organisation (Cipd, 2020). Workplace culture is also important as it impacts the standards of customer service and influence the retention of employees. Further, workplace culture affects the general performance of the organisation and thus the need to cultivate a positive work culture (Cipd, 2020). There are some common traits or values that are associated with healthy workplace culture including accountability, expression, equity, communication and recognition (Indeed Editorial Team, 2021). Consequently, healthy workplace culture is associated with better hiring choices, performance quality, organisational reputation and employee happiness (Indeed Editorial Team, 2021).
AC 2.2 Explain how organisations are whole systems, and how work and actions as a people professional could impact elsewhere.
Organisations are equated to whole systems as they compromise of several departments that conduct different functions but are united by a common organisational goal and function. Levinson (2018) explained that organisational systems simply refer to the general set up of a company. In this regard, organisations as a whole system defines the structure of the company in cognizance of each division or department and the hierarchy structure that determines who reports to who and what is expected of each of the divisions (Levinson, 2018).
Irrespective of size, all organisations require a solid and well defined system that outline simple processes that employees should adhere and thus avoid confusion at the workplace. The lack of a concrete and functional system the workplace becomes chaotic (Levinson, 2018). The organisational system ensure that all employee are assigned to the correct department and thus contribute towards the growth of the company.
The Human resource department plays a significant role in building a robust organisational system. Bianca (2019) indicated that human resource managers are in charge of the most significant of component of a successful business which is to recruit a productive and thriving workforce for each of the departments in an organisation. To this end, people professionals view people as assets as opposed to cost in an organisation. The human resource department develop good practice by recruiting and hiring people with certain skills-set that meet organisational current and future goals, coordinate employee benefits as well as flexibly shift employee around in different departments depending on employee abilities and business priorities (Bianca, 2019). When people professionals are able build a concrete organisational system they eliminate challenges such as work duplication, employee frustration and conflict between different departments or positions
AC2.3 Discuss how people learn and develop in different ways relating this to organisational assessment of people’s skills and capabilities
Learning and development are terms that are often used interchangeably at the workplace Learning can be defined as work-based self-directed process that increased adaptive potential while development refers to a broader and long term process of acquiring knowledge and skills (Cipd, 2021). The main goal of learning and development is to change the behaviour of groups or individuals for the better such that they are able deliver their mandate more efficiently.
There are several methods through which individuals and groups learn and develop at the workplace including formal or informal techniques, digital or face to face, internal or external provision, direct learning at the workplace or away from the workplace and created or curated resources (Cipd, 2021). Some of the workplace learning and developments methods are onjob training, in house development programmes, coaching and mentoring, job rotation, secondment, project work and shadowing (Cipd, 2021).
Vulpen (2020) that one of the popular approach to organisation learning is the 70/20/10 model that denotes that seventy percent of learning is work-based and occurs informally through hand on experience through daily work routines. Subsequently, twenty percent of learning occurs through developmental relationships through peer feedback, coaching, collaboration and peer mentoring. Finally en percent of learning occurs through professional development courses or formal training techniques in an educational setting. This is demonstrated in figure one below
Fig 1: the 70/20/10 Model of Organisational Learning
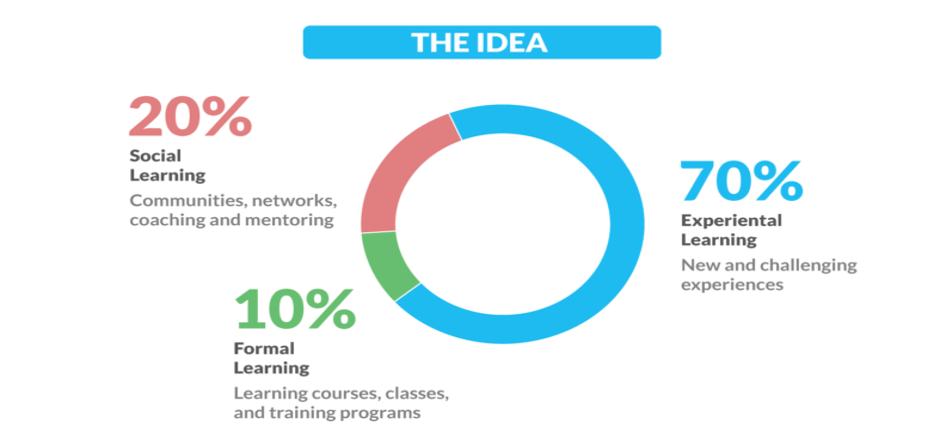
Prior to an organisation deciding on the learning and development method to use the organisation shoul evaluate the employees skills and competencies which can proceed through conducting of tests, getting feedback from teams, through self-assessment exercises, feedback from clients and engaging employees in a business game (Menshikov, 2017).
AC3.1 Explain the importance of planning and managing change within the workplace.
Business environments are regularly changing especially in today’s technological world. To this end, change management has been adopted by many organisations across the globe. Change management broadly defines the several ways that organisations prepare and implement simple or complex changes (Indeed Editorial Team, 2021). Michigan State University (2019) asserted that change management can be incremental that is evolutionary and internally driven or discontinuous that is revolutionary and externally driven.
Change management in organisations is important as any change that occurs impacts on all the employees. In addition, effective change management increases employee morale and drives team work among the employees. It also creates a positive environment for consistent evolution and thus facilitate general business change that allows the company to easily adopt new procedures and technologies (Michigan State University, 2019).
Change management is important as it assists each division of a company to succeed amidst major and minor adjustments within the company or business environment. Change management further allows employees to understand their new roles and thus execute their mandate efficiently and as per expectation. In general, change management in organisations ensures that businesses remain viable and thus continue to grow and align to the changing market trends (Indeed Editorial Team, 2021).
Change management is also attributed to reduce stress and anxiety with change, minimise resistance to change, enhances cooperation and collaboration in the business, responds to challenges more efficiently as well manages the diverse costs of change (Migrator, 2000).
AC3.2 Consider the importance and role that people professionals play within change.
According to Cipd (2020) people professionals have an important role in managing the change process in an organisations. This is because they are equated to stage directors of change serving behind the scenes and thus appreciated by all. The people professionals serve as the change agents in organisations due to their proximity to the people thus making it easy to influence leadership and provide an adequate framework that supports change within the workplace (Perrin, 2017).
In most organisations, the Human Resource department serves the role of a watchdog in change in management as it facilitates the implementation of new processes. In this regard, the HR takes up a monitoring role and also ensure that the change processes are harmonious, coherent and uphold integrity (Perrin, 2017).
People professionals also execute the role of communication in the change process as they clarify messages of change and ensure that people understand the process and comprehend the multiple avenues available to transmit the crucial messages. To this end, the HR utilises their knowledge and skills to minimise rumours by communicating through channels such as emails, formal briefs, podcasts and newsletter (Changeboard Team, 2016).
People professionals also have the role of diagnosing and planning change given that they are equipped with knowledge on the structure of change and thus have the skills to ask the right questions and diagnose the problems that might arise in the quest for change. Moreover, people professionals can assist in setting of expectations and ensuring that a comprehensive plan is laid out and thus creating an opportunity for the change architecture to be interrogated (Changeboard Team, 2019).
AC3.3 Discuss how change can impact people in different ways
Different people process and react to change differently. This is well captured by Owen (2018) who articulated that people react to change in different ways owing to their individual reasons giving cognizance to how that change impacts on their wellbeing. Owen (2018) indicated that some people thrive on change as they easily embrace new procedures and products while others initially resist change as the status quo is disrupted. In reference to a team, change can negatively affect employees as they are separated from each other and thus affect the efficiency of the team.
Additionally, change can creates uncertainty and anxiety which may be manifested through excessive worrying and changes in personal behaviours such as restlessness irritability and difficulty in concentrating. Other physical symptoms associated with anxiety include fidgeting, tiredness and trouble sleeping that are inevitably detrimental to employee productivity and performance (Owen, 2018). Change can also impact people financially as team restructuring for example may result in less overtime thus less money.
Change also positively or negatively affects employees trust and loyalty to the employer or organisation and thus impact on their job satisfaction, job attitude and organisational attitude (Owen, 2018). This can result in employees lacking confidence with the management and thus causing some of the employees to exit the organisation while others remain physically present but mentally searching for opportunities in other organisations thus diminishing their levels of productivity and involvement (Owen, 2018).
Wickford (2019) summarised the impacts of change to employees into increase in levels of stress due to fear of change, increased turnover as people exit the company in search of more stable organisations, diminished loyalty and increased time away from work as some employees avoid the office while looking for new jobs while other take longer lunch hours and leave the office earlier. However there are some employees who react by increasing their productivity as strategy of getting noticed and thus hoping that they will be retained amidst the change.
Bibliography
Bianca, A. (2019). The Components of Employee Retention & Career Development Processes. [online] Small Business – Chron.com. Available at: https://smallbusiness.chron.com/components-employee-retention-career-development-processes-12191.html.
Changeboard Team (2016). The role of HR in change. [online] Changeboard. Available at: https://www.changeboard.com/article-details/14013/the-role-of-hr-in-change/.
CIPD (2020a). Change Management | Factsheets. [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/change/management-factsheet#gref.
CIPD (2020b). Organisational Culture and Cultural Change | Factsheets. [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/culture/working-environment/organisation-culture-change-factsheet#gref.
CIPD (2021). Learning Methods | Factsheets. [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/people/development/learning-methods-factsheet#gref.
Indeed Editorial Team (2021a). Change Management: What It Is and Why It’s Important. [online] Indeed Career Guide. Available at: https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/change-management.
Indeed Editorial Team (2021b). What Is Work Culture? [online] Indeed Career Guide. Available at: https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/work-culture.
Levinson, C. (2018). The Structure of a Bureaucratic Organization. [online] Bizfluent. Available at: https://bizfluent.com/facts-6877710-structure-bureaucratic-organization.html.
Menshikov, S. (2017). Top 6 Ways To Assess Employee Skills And Competencies. [online] eLearning Industry. Available at: https://elearningindustry.com/top-6-ways-assess-employee-skills-and-competencies.
Michigan State University (2019). Organizational Change Management. [online] Michiganstateuniversityonline.com. Available at: https://www.michiganstateuniversityonline.com/resources/leadership/organizational-change-management/.
Migrator (2000). Benefits of change management. [online] nibusinessinfo.co.uk. Available at: https://www.nibusinessinfo.co.uk/content/benefits-change-management.
Owen, C. (2018). Explain possible human effects of innovation and change upon people and teams in an organisation. [online] Skills for Leadership. Available at: https://www.skillsforleadership.co.uk/explain-possible-human-effects-of-innovation-and-change-upon-people-and-teams-in-an-organisation/.
Perrin, O. (2017). The Role of HR in Managing Change in the Workplace. [online] EmployeeConnect HRIS. Available at: https://www.employeeconnect.com/blog/hr-role-change-management/.
Tarver, E. (2020). How to Tell If Your Corporate Culture Is Healthy. [online] Investopedia. Available at: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/corporate-culture.asp.
Vulpen, E.V. (2020). Learning and Development: A Comprehensive Guide. [online] AIHR. Available at: https://www.aihr.com/blog/learning-and-development/.
3CO01 Assignment PPT





Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Table of Contents
3CO01 Business Culture and Change in Context

Case study
You work in the HR Team of a medium sized organisation and are studying for your people practice qualification. In a recent discussion with your manager, you expressed how important you thought it was for employees to understand the business environment. You feel this is especially important for people practice professionals as their roles impact on the policies, processes and values of the organisation, which in turn impact on all the people within the organisation.
Inspired by this discussion, your manager has asked you to help prepare
development day. A team-based learning needs analysis has shown that as well as more knowledge about the business environment, the team would benefit from a deeper understanding of organisational culture and how humans behave in organisations. The team would also like to build their knowledge and skills in relation to change management.
Preparation for the Tasks:
- At the start of your assignment, you are encouraged to plan your assessment work with your Assessor, and, where appropriate, agree milestones, so that they can help you monitor your progress.
- Refer to the indicative content in the unit to guide and support your evidence.
- Pay attention to how your evidence is presented, remember you are working in the People Practice Team.
- Ensure that the evidence generated for this assessment remains your own work.
You will also benefit from:
- Completing and acting on formative feedback from your Assessor.
- Reflecting on your own experiences of learning opportunities and continuing professional development.
- Reading the CIPD Insight, Fact Sheets and related online materials on these topics.
Task One-Slide Deck for Team Day
Your manager has asked you to prepare a presentation (slide deck and brief presenter notes) in readiness for delivery to the HR Team at the next Team day. The aim of the presentation, entitled
is for team members to gain a general understanding of their business environment and the key issues that can affect this.
Your presentation (which you are not required to deliver) can be based on your own organisation or one(s) that you are familiar with, and should include the following:
- Application of an analysis tool (such as PESTLE) to examine the key external forces impacting or likely to impact an ties. (AC 1.1)
- An explanation of business goals and why it is important for organisations to plan for how they will achieve these. Your explanation should include examples of planning, such as how a business has been structured or specific policies introduced or people practices followed, in order for business goals to be achieved. (AC 1.2)
- An explanation of an organisation s products and/or services and main customers. (AC 1.3)
- A short review of different technologies available to people professionals and how these can be used to improve working practices and collaboration. You might consider for example, technologies relating to communications, information sharing, record keeping, learning, wellbeing, productivity or security. (AC 1.4)
Task Two Guidance Leaflet
In line with the team learning need analysis and knowing that they will be required to support a number of change initiatives soon, your manager has also asked you to prepare a guidance leaflet for the team. The guidance leaflet should cover two main themes and include
- information about organisational culture and how people behave in organisations
- guidance about the impact of change and how organisational change can most effectivelybe managed.
Your guidance leaflet should explain (in any sequence):
- What is meant by workplace (organisation) culture (AC 2.1)
- Why it is important to foster an appropriate and effective workplace culture. (AC 2.1)
- How organisations are whole systems in which different areas and aspects such as structure, systems and culture, are all inter-related. (AC 2.2)
- An example of how good people practice, and an example of how bad people practice can impact other parts of the organisation or beyond the organisation (for example through developing new and better ways of doing things or through poor practice stimulating new legislation). (AC 2.2)
- How individuals may learn and develop in different ways in organisations and how this might be accommodated in assessing and developing skills and capabilities. (AC 2.3)
- Why it is important for an organisation that change is predicted, planned and effectively managed. (AC 3.1)
- How change can impact people in organisations, such as changing their role or status or financial situation, and the different ways people may respond to change. (AC 3.3)
- The nature and importance of different roles that can be played by people practice professionals, in relation to change agendas. You might consider roles such as: gatekeeper, champion, facilitator, critical friend or record-keeper. (AC 3.2)
Solution Task One
AC 1.1 Examine the key external influences that impact on business environments

Organisations do not operate in a vacuum rather their operations are influenced by external forces in their business worlds. To this end, there exists several tools that help in the analysis of external factors that affect business in all sectors including the hospitality industry that forms the core of our business. Among such tools is the PESTLE analysis that is an acronym for Political, Economic, Sociological, Technological, Legal and Environmental. Cipd (2021) defines the PESTLE analysis as a strategic, broad fact finding activity of the external factors that potentially influence the decisions of companies by assisting to minimise the threats and subsequently maximise on the available opportunities. The following is analysis of the factors within the hospitality industry
- Political factors that influence the industry include environmental regulations, tax policy, trade restrictions, political stability and tariffs. This has been evidence during the Covid19 pandemic period as many governments imposed travel bans that negatively affected the industry Frue (2019). Similarly, the hospitality industry operates in fear during presidential elections as new governments could introduce new ideas and policies that impact on the industry and disrupts the operations.
- Economic factors that influence the industry include economic growth or decline, inflation, interest, wage rates, exchange rate, minimum wage, working hours, cost of living, availability of credit and unemployment. In this regard, the strength or weakness if a currency can affect the attractiveness of a vacation destination. The short term impact of Brexit was loss of a substantial number of employees from other EU countries (James, 2021).
- Sociological factors include cultural norms, health consciousness, career attitudes, age distribution population growth rates, health and safety. For example, consumers have become more health conscious during the Covid19 pandemic period and hence the industry investment on sanitising procedures for their facilities.
- Technological factors include new technologies for example robotics and rate of change (Cipd, 2021). To this end, some hotels have adopted robotics in sanitising their facilities which is faster and more efficient. The industry is also investing in social media and working towards getting positive reviews on travelling websites ( Frue, 2019)
- Legal factors include changes to legislations such as employment, imports/exports, access to quotas, materials and taxation (Cipd, 2021)
- Environmental factors include ethical sourcing, global warming, pandemics and other emergencies. Frue (2019) noted that the industry have to understand the seasonal or weather differences to competitively price their rooms.
AC 2.1 Discuss organisational goals and why it is important for organisations to plan.

According to Hill (2019) planning is a process that charts a course for attainment of defined business goals. The process entails conducting a review of operations of the organisation and subsequently identifying what needs to be improved in the next year. As such planning necessitates forecasting of the results that an organisation desires to achieve and identifying the measures to be taken in order to attain the set goals. The results can be can be in financial terms or other measures such as consumer satisfaction (Hill, 2019).
Scott (2010) explained that human resources personnel have different functions in organisations including ensuring that there policies put in place to ensure that employees are responsible for the attainment of organisational objectives and goals. Giving reference to the hospitality industry, it is broadly structured into food and beverages, travel and tourism, lodging and recreation (Novak, 2017). Their ultimate goal is to create a positive customer experience so as retain the consumer in future or even gain a referral.
In line with this, the HR department training and development plans within the hospitality industry seeks to invest in imparting the right knowledge and skills to the employees who are the direct link between an organisation and the company. Scott (2010) detailed that HR professionals are charged with responsibility of developing training and development programs that strengthen the quality of work in a company. This proceed upon evaluating the training needs, developing manuals, facilitating instruction and ascertaining that training objectives align to the business goals. Scott (2010) highlight the findings of the Bureau of Labor statistics denoting that imparting employees with skills can enhance organisational performance and help achieve business results.
AC 1.3 Discuss the products and/or services the organisation delivers, including who the main customers are

Bansal, Gaulum, Anbardar and Kumar (n.d.) cited Philip Kotler’s definition of a product as a bundle of a physical service and symbolic particulars that are anticipated to be beneficial to the buyer or yield satisfaction to a consumer.
The hospitality industry has five components of hospitality products including core products that refers to the basic benefit accorded to a guest such as a place to eat. The second is facilitating products that refers to those products that are provided to a guest in order to utilise the core product such as food in case of restaurants. Consequently, there are tangible products that refer to physical products of hospitality such as television and air conditioning in a standard room. There are supporting products that are provided to increase the value of the basic product with the intention of making it unique. Last but not least are augmented products refers to the products that are essential in enhancing the quality of products devoid of additional charges.
On the other hand, Bansal et al. (n.d.) defined services as the intangible activities that provide want satisfaction. It is also defined as any activity that one party offers to another and does not yield to ownership. Services can also be articulated as intangible economic products that involves human beings serving the provider and the recipient. They have several traits such as they are perishable, they lack physical identity, they are inseparable, have high fixed costs and are interdependent.
Capozzi (2020) argued that consumers in the hospitality industry can be categorised into backpackers and solo travellers that enjoy exploring cities and spending time in hotels and thus choose low prices over services and amenities. The other category is couples that involves romantic partners seeking quiet premises and high quality bedding. The other group is families that have more specific needs such as on site play areas, discounts for kids’ rooms, entertainment and additional amenities such as booster chairs. Business travellers is the final category and requires fast internet access, electronics such as printers and are usually willing to pay a higher price for rooms.
AC 1.4 Review the range of technology available within the people profession, including how it can be utilised to improve working practices and collaboration

As the world and the workplace become increasingly digitised HR managers are also forced to adapt to new technology that has enhanced their work. Technology is utilised in managing information on the cloud, engaging with people on social media sites and working on the go through tablets and mobiles (Barcelos, 2018).the following are some of the technology pieces required by people professionals
- Social media platforms such as Facebook, twitter and LinkedIn and are used for posting vacant positions, communicate on upcoming events to the public and helps in making decisions on the right fit for a company
- Human Resources Information Software (HRIS) helps in streamlining several HR processes and tasks that diminish manual errors. Besides automating HR functions it also helps in easier management of HR documents
- Cloud technology that assists in centralisation of business and HR data from payroll to feedback, enhances transparency within the organisation and boosts consistency.
- Gamification techniques that are utilised in recruitment to enhance talent acquisition. It is also used to enhance learning and development through knowledge sharing and simulation of real life contexts.
(Adapted from Bercelos, 2018).
Bibliography
Barcelos, K. (2018). Top 6 Technology Skills Every HR Professional Needs Today. [online] AIHR. Available at: https://www.aihr.com/blog/technology-skills-every-hr-professional-needs/.
Capozzi, C. (2020). Service Marketing vs. Product Marketing in Hotels. [online] Small Business – Chron.com. Available at: https://smallbusiness.chron.com/service-marketing-vs-product-marketing-hotels-23637.html.
Frue, K. (2019). PESTLE Analysis for Hotel Industry. [online] PESTLE Analysis. Available at: https://pestleanalysis.com/pestle-analysis-for-hotel-industry/.
Hill, B. (2019). How to Analyze the Key Success Factors for Plan Implementation. [online] Small Business – Chron.com. Available at: https://smallbusiness.chron.com/analyze-key-success-factors-plan-implementation-47365.html.
James, W. (2021). The impact of Brexit on the hospitality sector; what’s the post-Brexit outlook? [online] Stint. Available at: https://stint.co/learning-hub/the-impact-of-brexit-on-the-hospitality-sector/.
Novak, P. (2017). What Are The 4 Segments Of The Hospitality Industry. [online] Hospitality Net. Available at: https://www.hospitalitynet.org/opinion/4082318.html.
Scott, S. (2010). Role of HR in Achieving Business Goals. [online] Chron.com. Available at: https://smallbusiness.chron.com/role-hr-achieving-business-goals-1767.html.
Solution Task Two
AC 2.1 Define workplace culture in organisational settings and the importance of fostering positive approaches towards it.
Workplace culture in organisations can be defined as the set of underlying beliefs, principles and values that serve as the cornerstone of a company’s management system. It is also inclusive of the management behaviours and practices adopted in reinforcing the basic beliefs (Cipd, 2020). Tarver (2021) defined corporate culture as the beliefs and behaviours that guide how employees and the management interact and conduct business transactions. Tarver (2021) emphasized that corporate culture though not expressly defined it is implied and organically develops over time as an organisation hires people that represent it. The culture at the workplace is demonstrated by business hours, hiring decisions, dress code, and treatment of consumers, office set up, consumer satisfaction, employee benefits and turnover.
Workplace culture offers employee a way to understand the company, develop a network and common purpose as well as voice their views in reference to the mission of the organisation (Cipd, 2020). Workplace culture is also important as it impacts the standards of customer service and influence the retention of employees. Further, workplace culture affects the general performance of the organisation and thus the need to cultivate a positive work culture (Cipd, 2020). There are some common traits or values that are associated with healthy workplace culture including accountability, expression, equity, communication and recognition (Indeed Editorial Team, 2021). Consequently, healthy workplace culture is associated with better hiring choices, performance quality, organisational reputation and employee happiness (Indeed Editorial Team, 2021).
AC 2.2 Explain how organisations are whole systems, and how work and actions as a people professional could impact elsewhere.
Organisations are equated to whole systems as they compromise of several departments that conduct different functions but are united by a common organisational goal and function. Levinson (2018) explained that organisational systems simply refer to the general set up of a company. In this regard, organisations as a whole system defines the structure of the company in cognizance of each division or department and the hierarchy structure that determines who reports to who and what is expected of each of the divisions (Levinson, 2018).
Irrespective of size, all organisations require a solid and well defined system that outline simple processes that employees should adhere and thus avoid confusion at the workplace. The lack of a concrete and functional system the workplace becomes chaotic (Levinson, 2018). The organisational system ensure that all employee are assigned to the correct department and thus contribute towards the growth of the company.
The Human resource department plays a significant role in building a robust organisational system. Bianca (2019) indicated that human resource managers are in charge of the most significant of component of a successful business which is to recruit a productive and thriving workforce for each of the departments in an organisation. To this end, people professionals view people as assets as opposed to cost in an organisation. The human resource department develop good practice by recruiting and hiring people with certain skills-set that meet organisational current and future goals, coordinate employee benefits as well as flexibly shift employee around in different departments depending on employee abilities and business priorities (Bianca, 2019). When people professionals are able build a concrete organisational system they eliminate challenges such as work duplication, employee frustration and conflict between different departments or positions
AC2.3 Discuss how people learn and develop in different ways relating this to organisational assessment of people’s skills and capabilities
Learning and development are terms that are often used interchangeably at the workplace Learning can be defined as work-based self-directed process that increased adaptive potential while development refers to a broader and long term process of acquiring knowledge and skills (Cipd, 2021). The main goal of learning and development is to change the behaviour of groups or individuals for the better such that they are able deliver their mandate more efficiently.
There are several methods through which individuals and groups learn and develop at the workplace including formal or informal techniques, digital or face to face, internal or external provision, direct learning at the workplace or away from the workplace and created or curated resources (Cipd, 2021). Some of the workplace learning and developments methods are onjob training, in house development programmes, coaching and mentoring, job rotation, secondment, project work and shadowing (Cipd, 2021).
Vulpen (2020) that one of the popular approach to organisation learning is the 70/20/10 model that denotes that seventy percent of learning is work-based and occurs informally through hand on experience through daily work routines. Subsequently, twenty percent of learning occurs through developmental relationships through peer feedback, coaching, collaboration and peer mentoring. Finally en percent of learning occurs through professional development courses or formal training techniques in an educational setting. This is demonstrated in figure one below
Fig 1: the 70/20/10 Model of Organisational Learning

Prior to an organisation deciding on the learning and development method to use the organisation shoul evaluate the employees skills and competencies which can proceed through conducting of tests, getting feedback from teams, through self-assessment exercises, feedback from clients and engaging employees in a business game (Menshikov, 2017).
AC3.1 Explain the importance of planning and managing change within the workplace.
Business environments are regularly changing especially in today’s technological world. To this end, change management has been adopted by many organisations across the globe. Change management broadly defines the several ways that organisations prepare and implement simple or complex changes (Indeed Editorial Team, 2021). Michigan State University (2019) asserted that change management can be incremental that is evolutionary and internally driven or discontinuous that is revolutionary and externally driven.
Change management in organisations is important as any change that occurs impacts on all the employees. In addition, effective change management increases employee morale and drives team work among the employees. It also creates a positive environment for consistent evolution and thus facilitate general business change that allows the company to easily adopt new procedures and technologies (Michigan State University, 2019).
Change management is important as it assists each division of a company to succeed amidst major and minor adjustments within the company or business environment. Change management further allows employees to understand their new roles and thus execute their mandate efficiently and as per expectation. In general, change management in organisations ensures that businesses remain viable and thus continue to grow and align to the changing market trends (Indeed Editorial Team, 2021).
Change management is also attributed to reduce stress and anxiety with change, minimise resistance to change, enhances cooperation and collaboration in the business, responds to challenges more efficiently as well manages the diverse costs of change (Migrator, 2000).
AC3.2 Consider the importance and role that people professionals play within change.
According to Cipd (2020) people professionals have an important role in managing the change process in an organisations. This is because they are equated to stage directors of change serving behind the scenes and thus appreciated by all. The people professionals serve as the change agents in organisations due to their proximity to the people thus making it easy to influence leadership and provide an adequate framework that supports change within the workplace (Perrin, 2017).
In most organisations, the Human Resource department serves the role of a watchdog in change in management as it facilitates the implementation of new processes. In this regard, the HR takes up a monitoring role and also ensure that the change processes are harmonious, coherent and uphold integrity (Perrin, 2017).
People professionals also execute the role of communication in the change process as they clarify messages of change and ensure that people understand the process and comprehend the multiple avenues available to transmit the crucial messages. To this end, the HR utilises their knowledge and skills to minimise rumours by communicating through channels such as emails, formal briefs, podcasts and newsletter (Changeboard Team, 2016).
People professionals also have the role of diagnosing and planning change given that they are equipped with knowledge on the structure of change and thus have the skills to ask the right questions and diagnose the problems that might arise in the quest for change. Moreover, people professionals can assist in setting of expectations and ensuring that a comprehensive plan is laid out and thus creating an opportunity for the change architecture to be interrogated (Changeboard Team, 2019).
AC3.3 Discuss how change can impact people in different ways
Different people process and react to change differently. This is well captured by Owen (2018) who articulated that people react to change in different ways owing to their individual reasons giving cognizance to how that change impacts on their wellbeing. Owen (2018) indicated that some people thrive on change as they easily embrace new procedures and products while others initially resist change as the status quo is disrupted. In reference to a team, change can negatively affect employees as they are separated from each other and thus affect the efficiency of the team.
Additionally, change can creates uncertainty and anxiety which may be manifested through excessive worrying and changes in personal behaviours such as restlessness irritability and difficulty in concentrating. Other physical symptoms associated with anxiety include fidgeting, tiredness and trouble sleeping that are inevitably detrimental to employee productivity and performance (Owen, 2018). Change can also impact people financially as team restructuring for example may result in less overtime thus less money.
Change also positively or negatively affects employees trust and loyalty to the employer or organisation and thus impact on their job satisfaction, job attitude and organisational attitude (Owen, 2018). This can result in employees lacking confidence with the management and thus causing some of the employees to exit the organisation while others remain physically present but mentally searching for opportunities in other organisations thus diminishing their levels of productivity and involvement (Owen, 2018).
Wickford (2019) summarised the impacts of change to employees into increase in levels of stress due to fear of change, increased turnover as people exit the company in search of more stable organisations, diminished loyalty and increased time away from work as some employees avoid the office while looking for new jobs while other take longer lunch hours and leave the office earlier. However there are some employees who react by increasing their productivity as strategy of getting noticed and thus hoping that they will be retained amidst the change.
Bibliography
Bianca, A. (2019). The Components of Employee Retention & Career Development Processes. [online] Small Business – Chron.com. Available at: https://smallbusiness.chron.com/components-employee-retention-career-development-processes-12191.html.
Changeboard Team (2016). The role of HR in change. [online] Changeboard. Available at: https://www.changeboard.com/article-details/14013/the-role-of-hr-in-change/.
CIPD (2020a). Change Management | Factsheets. [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/change/management-factsheet#gref.
CIPD (2020b). Organisational Culture and Cultural Change | Factsheets. [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/culture/working-environment/organisation-culture-change-factsheet#gref.
CIPD (2021). Learning Methods | Factsheets. [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/people/development/learning-methods-factsheet#gref.
Indeed Editorial Team (2021a). Change Management: What It Is and Why It’s Important. [online] Indeed Career Guide. Available at: https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/change-management.
Indeed Editorial Team (2021b). What Is Work Culture? [online] Indeed Career Guide. Available at: https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/work-culture.
Levinson, C. (2018). The Structure of a Bureaucratic Organization. [online] Bizfluent. Available at: https://bizfluent.com/facts-6877710-structure-bureaucratic-organization.html.
Menshikov, S. (2017). Top 6 Ways To Assess Employee Skills And Competencies. [online] eLearning Industry. Available at: https://elearningindustry.com/top-6-ways-assess-employee-skills-and-competencies.
Michigan State University (2019). Organizational Change Management. [online] Michiganstateuniversityonline.com. Available at: https://www.michiganstateuniversityonline.com/resources/leadership/organizational-change-management/.
Migrator (2000). Benefits of change management. [online] nibusinessinfo.co.uk. Available at: https://www.nibusinessinfo.co.uk/content/benefits-change-management.
Owen, C. (2018). Explain possible human effects of innovation and change upon people and teams in an organisation. [online] Skills for Leadership. Available at: https://www.skillsforleadership.co.uk/explain-possible-human-effects-of-innovation-and-change-upon-people-and-teams-in-an-organisation/.
Perrin, O. (2017). The Role of HR in Managing Change in the Workplace. [online] EmployeeConnect HRIS. Available at: https://www.employeeconnect.com/blog/hr-role-change-management/.
Tarver, E. (2020). How to Tell If Your Corporate Culture Is Healthy. [online] Investopedia. Available at: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/corporate-culture.asp.
Vulpen, E.V. (2020). Learning and Development: A Comprehensive Guide. [online] AIHR. Available at: https://www.aihr.com/blog/learning-and-development/.
3CO01 Assignment PPT






