5OS02 Assignment Example
- March 25, 2022
- Posted by: Assignment Help Gurus
- Category: CIPD CIPD Level 5 HUMAN RESOURCE
5OS02 Advances in digital learning and development
Case study
You are a learning and development consultant who has been contracted by a relatively large organisation that, in the past, outsourced its L&D function. It is now looking to expand its in-house L&D offering and is keen to utilise the new learning technologies that are available. You have effectively been given a ‘clean sheet’ in which to work from, as the only people directly involved will be you and a newly appointed L&D Manager.
The task, as described by the People Director in their Annual Plan to the Board, is to look at how the organisation can “do L&D differently and deliver to the masses”.
For Task 1, you have been asked to create a presentation to be delivered at the organisation’s Annual Conference, which will be attended by all senior leaders and managers of the organisation. Your presentation will introduce them to the concepts of ‘Digital Learning & Development Transformation’.
Preparation for tasks:
- At the start of the assignment, you are encouraged to plan your assessment work with your assessor and, where appropriate, agree milestones so that they can help you monitor your progress
- Refer to the indicative content in the unit guide and support your evidence
- Pay attention to how your evidence is presented, remember you are working in the People Development Team for this task
- Ensure that the evidence generated for this assessment remains your own work
You will also benefit from:
- Acting on formative feedback from your assessor
- Reflecting on your own experiences of learning opportunities, training and continuing professional development
- Utilising CIPD factsheets, reports and podcasts, as well as any other online material on these topics
Task 1 – Annual conference presentation pack and supporting notes
You need to create a 20-minute presentation for the organisation’s annual conference. This will be shared among all attending senior leaders and managers within the organisation to help them understand the digital learning and development transformation that you will be leading within the organisation over the next 18 months. As part of this activity, you will need to:
- Evaluate how the development of technology, along with digital collaboration, has impacted the design and delivery of learning and development over the past five years (AC 1.1).
- Evaluate at least one risk and one challenge that technology-based learning and development poses to:
- Organisations, and how these could be addressed (part of AC 1.2)
- L&D professionals, and how these could be addressed (part of AC 1.2)
- Learners, and how these could be addressed (part of AC 1.2)
- Assess the following five different types of digital learning content, ‘explainer videos’, PDFs, infographics, e-learning and scenarios. Discuss when these types may be applied in learning and add in an overview as to the benefit the learner receives from this type of digital learning content (AC 2.1).
- Evaluate three attributes that you would consider to help you to choose the right digital learning content to maximise the impact on learner engagement and how you would ensure that the content meets the identified learning need (AC 2.2).
| Your evidence must consist of: |
| PowerPoint Presentation Slide Deck and supporting notes of around 2,300 (+ or – 10%)
A maximum 20-minute PowerPoint Presentation. (You do not have to deliver this presentation in the real world or video yourself delivering it). |
Task 2 – “Showcasing” digital facilitated learning using a live online learning system
The content of this digital facilitated presentation could be directed towards any learning topic, outcome, or objective of your choice.
However, if you are struggling for ideas, you could choose any topic from the Fire Safety at Work topic list below, covering any topic of your choice from those listed below:
- Legal responsibility under the Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005
- Fire prevention covering relevant aspects related to your business and premises
- Live Fire Simulator and use of Fire Extinguishers* (Digital Online Synchronous Session)
- Real-life case studies
- Fire safety checklists
- The ‘fire triangle’ and the spread of fire
- Electrical safety in the workplace
- Compartmentation in properties
- Kitchen fire safety
- Improving fire safety
- Evacuation strategies
- Fire service/brigade liaison and requirements
- Grab bags and their importance
- PEEP (Personal Emergency Evacuation Plans)
- COSHH/DSEAR regulations
- Comprised escape route strategies including safe room
Part A – Digital Facilitated Presentation
As part of this activity, you will need provide
- Demonstrate online facilitation skills within a live online learning activity where (AC 3.4)
Part B – A written response to the following Assessment Criteria:
Considering the online delivery method, (these could be Cisco Webex, Adobe Connect, Microsoft Teams, GoToMeeting, or others of your choice), that you may, or could, have used for your Digital Facilitated Presentation, compare two other potential systems for delivering live online learning activities. The comparison should include:
- Their key ‘facilitation functions’, or functionalities, and their strengths and weaknesses as live online learning delivery methods (AC 3.1)
- Discuss how facilitation of a live online learning activity can differ from facilitation of a face-to-face learning activity and the implications of this for: (AC 3.2)
- Facilitators
- Learners
- Learning administration
- Assess three main facilitation skills required to facilitate live online learning, then pick one that you wish to develop further and provide yourself with a SMART Development Objective to add to your PDP in support of that knowledge/skill development (AC3.3)
SOLUTION
5OS02 ASSIGNMENT ANSWERS
Task 1
AC 1.1: The Impact of Technology and Digital Collaboration on L&D

Over the past five years, the advancement of technology and digital collaboration has exerted a noteworthy influence on the design and implementation of learning and development (L&D) initiatives. There exist several significant ways in which technology has exerted its influence on the field of learning and development (L&D).
- Increased Accessibility: The rise of technology has resulted in enhanced accessibility, thereby broadening the reach of educational opportunities to a more diverse range of individuals. The proliferation of mobile devices and online platforms has facilitated the prevalent availability of training materials, enabling learners to access them at their convenience and from any location. According to Glenister (2020), the utilisation of this technology has facilitated the ability of organisations to effectively engage with geographically dispersed employees and offer flexible learning opportunities.
- Personalised Learning: The utilisation of technology enables the tailoring of educational experiences to individual learners. Organisations have the ability to provide customised content to learners by utilising learning management systems (LMS) and adaptive learning platforms. The customization is based on the individual needs, preferences, and progress of the learners (Glenister, 2020). The incorporation of personalization strategies has been found to have a positive impact on engagement levels and knowledge retention.
- Improved Interactivity: The advent of digital tools and platforms has resulted in an increased level of interactivity that has enhanced the overall engagement of learners. The utilisation of gamification, virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and simulations offer learners the opportunity to engage in immersive experiences that facilitate the practical application of their acquired knowledge within realistic contexts (Glenister, 2020). This leads to heightened levels of engagement and enhanced proficiency in skill acquisition.
- Increased utilisation of data to drive impact: The utilisation of technology facilitates the gathering and examination of data pertaining to educational endeavours. The utilisation of learning analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) enables the monitoring of learners’ advancement, identification of areas of insufficient knowledge, and provision of tailored recommendations for individualised learning trajectories (Glenister, 2020). These observations assist professionals in the field of Learning and Development (L&D) in enhancing learning outcomes by optimising both the content and delivery methods.
- Increased collaboration: Collaborative learning is enhanced through the utilisation of digital collaboration tools, such as discussion forums, video conferencing, and social learning platforms. These tools effectively facilitate the sharing of knowledge and promote collaborative learning experiences, Glenister (2020). Individuals engaged in the learning process have the opportunity to establish connections with fellow learners, experts in the field, and trainers. This facilitates the development of a culture that promotes ongoing learning and the exchange of knowledge.
AC 1.2: Risks and Challenges of Technology-Based L&D

Although technology-based learning and development present a multitude of advantages, it is imperative to acknowledge and confront the associated risks and challenges it poses to organisations, L&D professionals, and learners.
- Organisations
One potential risk that should be considered is the possibility of failures in technological infrastructure and systems. As organizations increasingly rely on technology to support their operations and digital learning initiatives, it becomes imperative for them to guarantee the robustness, security, and capability of their IT infrastructure. Any disruption or malfunction in the infrastructure can have a significant impact on the organization’s ability to effectively deliver digital learning programs and materials. Therefore, organizations need to invest in reliable and resilient technological infrastructure to minimize the risk of system failures.
In addition to technological challenges, organizations may also face resistance to change from employees who lack familiarity with or exhibit resistance towards technology. Some individuals may be reluctant to adopt digital learning methods and prefer traditional approaches. This resistance can hinder the successful implementation of digital learning initiatives. To mitigate these potential risks, organizations should allocate resources toward the acquisition of dependable technological infrastructure that is user-friendly and intuitive. Moreover, comprehensive training and support should be provided to employees throughout the transitional period to ensure they have the necessary skills and knowledge to embrace digital learning effectively.
- Learning and Development (L&D) Professionals
The utilization of technology-based resources presents specific challenges for professionals in the field of Learning and Development (L&D). As digital tools and platforms become integral to delivering educational content, L&D professionals may be required to acquire additional skills and knowledge to effectively utilize these technologies (Manning, 2021). They need to adapt to new instructional design principles, digital content creation, and data analysis techniques to maximize the benefits of digital learning.
There is also a concern regarding job displacement as a result of automation. With the increasing use of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms in educational settings, certain tasks traditionally performed by L&D professionals may become automated. This shift can potentially impact the job market for L&D professionals and require them to upskill or reskill to remain relevant in the digital era. Organizations should address this concern by offering professional development opportunities specifically tailored to enhance the digital skills of L&D professionals (Manning, 2021). By continuously updating their expertise in digital learning methodologies and staying abreast of emerging technologies, L&D professionals can proactively adapt to the changing landscape and contribute to the successful implementation of digital learning initiatives.
To ensure the quality of digital content, organizations should establish standards and guidelines for developing and evaluating digital learning materials. This includes validating the accuracy and reliability of the content, assessing its relevance to the learning objectives, and ensuring its accessibility for diverse learners. By maintaining high standards for digital content, organizations can instil confidence in learners and ensure that the digital learning experience meets their educational needs effectively (Manning, 2021).
- Learners
Learners themselves may encounter various difficulties when engaging in digital learning. Digital literacy, or the ability to use digital tools and navigate online platforms, can be a barrier for some individuals. Not everyone possesses the same level of proficiency when it comes to using technology for learning purposes. Organizations should address this challenge by implementing measures such as providing digital literacy training programs. These programs can help learners develop the necessary skills to navigate digital platforms, access online resources, and effectively utilize digital tools for their learning needs.
Another challenge for learners is the availability of technology and reliable internet connectivity. Not all employees have equitable access to digital devices or a stable internet connection, which can limit their ability to participate in digital learning activities. To promote equitable access, organizations should consider providing resources such as loaner devices or subsidies for purchasing technology, as well as ensuring access to reliable internet connections. By removing these barriers, organizations can create an inclusive learning environment where all learners have equal opportunities to engage in digital learning.
Furthermore, certain individuals may struggle with self-regulated learning in a digital setting. Digital learning often requires learners to take more ownership of their learning process and be proactive in managing their time and resources. Some learners may find it challenging to stay motivated, set goals, and organize their learning activities without the structure and guidance provided in traditional classroom settings. To support learners in self-directed learning, organizations can establish support mechanisms such as online tutorials, mentoring programs, and peer-to-peer collaboration platforms. These resources can provide learners with guidance, feedback, and opportunities for interaction, facilitating their engagement and success in digital learning environments.
AC 2.1: Types of Digital Learning Content and Benefits
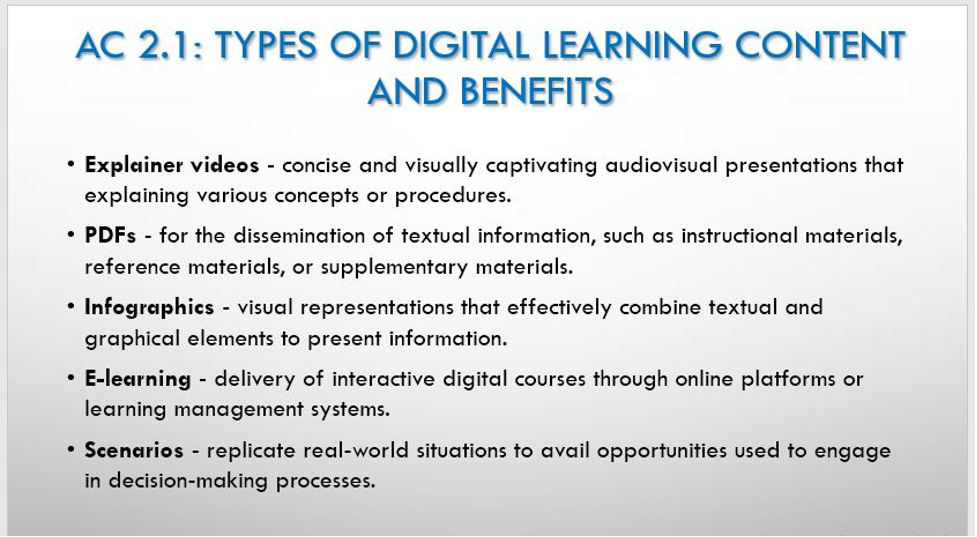
- Explainer Videos – refer to concise and visually captivating audio-visual presentations that serve the purpose of explaining various concepts or procedures. They are efficient in simplifying intricate subjects, acquainting individuals with new concepts, or illustrating methodologies. Explainer videos offer learners a valuable advantage by providing an easy-to-understand and visually captivating medium through which to efficiently comprehend information (Schorn, 2022).
- PDFs: Also known as Portable Document Format, are extensively utilised for the dissemination of textual information, such as instructional materials, reference materials, or supplementary materials (Fedoruk, 2022). They are convenient for disseminating comprehensive information, allowing learners to engage with the material at their preferred speed. PDFs offer learners convenient access to reference materials that can be saved or printed for offline utilisation.
- Infographics: refer to visual representations that effectively combine textual and graphical elements to present information or convey concepts. These tools demonstrate efficacy in condensing intricate data, displaying statistical information, and elucidating procedural concepts. According to Neelakandan (2019), infographics have the ability to captivate learners by presenting information in a visually appealing and easily comprehensible manner.
- E-learning: E-learning encompasses the delivery of interactive digital courses through online platforms or learning management systems. E-learning modules can incorporate various multimedia components, as well as interactive quizzes and assessments. According to the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO, 2011), e-learning offers advantages to learners through the provision of self-paced learning opportunities, interactive content, and immediate feedback.
- Scenarios: They are instructional tools that replicate real-world situations and provide learners with opportunities to engage in decision-making processes (Ivec, 2021). Learners actively participate in scenarios through the process of analysing the contextual factors, identifying various options, and evaluating the potential consequences. Scenarios facilitate the development of critical thinking abilities, problem-solving aptitude, and the practical application of acquired knowledge (Ivec, 2021).
AC 2.2: Attributes for Choosing Digital Learning Content

When making choices regarding digital learning content to optimise learner engagement, both organisations and individuals need to take into account several key attributes:
- Relevance of the material to be used
Organisations need to create parameters that allow them to select material that is in line with the identified educational or organisational requirements and goals. When selecting learning material, it is essential to ensure that it directly relates to the learners’ respective roles, tasks, and responsibilities (Sethu, 2021). The content chosen should provide practical knowledge and skills that can be applied in real-world work environments. Research has shown that when learners perceive the relevance of the material, it positively impacts their motivation levels and their ability to transfer what they have learned into their job performance (Sethu, 2021). By aligning the content with learners’ needs and goals, organisations can enhance the effectiveness and applicability of the learning experience.
- Level of interactivity
It is vital for organisations to select content or learning material that actively promotes active participation and engagement among employees throughout the learning and development process (Sethu, 2021). Passive learning experiences, such as reading static text or listening to lectures, often result in limited engagement and reduced knowledge retention. On the other hand, interactive components within the learning material, such as quizzes, simulations, and gamified activities, encourage learners to actively participate and apply their knowledge in practical scenarios. These interactive elements facilitate learner engagement, enhance knowledge retention, and foster the development of skills (Sethu, 2021). Additionally, they provide opportunities for immediate feedback, allowing learners to assess their understanding and make necessary adjustments. Moreover, interactive learning experiences encourage collaboration among learners, enabling them to interact with and learn from each other’s experiences and perspectives (Sethu, 2021). This collaborative aspect promotes a sense of community and enhances the overall learning process.
- Multimedia Elements
Organisations need to find ways to integrate a diverse range of multimedia elements into their learning and development (L&D) activities. By incorporating different media formats, such as videos, images, audio, and animations, organisations can enhance the educational experience and cater to various learning styles. Well-crafted visual aids and captivating multimedia components have the potential to improve understanding, memory retention, and overall learner involvement (Sethu, 2021). For instance, videos can provide real-life examples and demonstrations, making complex concepts more accessible and relatable. Images can help illustrate key points and enhance comprehension. Audio elements, such as narration or podcasts, can provide additional explanations or create a more immersive learning environment. Animations can visually depict processes or concepts that are difficult to grasp through text alone. By utilizing a combination of multimedia elements, organisations can offer learners multiple means of accessing educational materials, accommodating different learning preferences and maximizing the effectiveness of the learning experience.
To ensure that the selected digital learning content aligns with the identified learning needs, it is advisable to take into account the following steps:
- Perform a Needs Analysis: begin the process by conducting a comprehensive needs analysis in order to ascertain the precise learning requirements and objectives for both the individual and the organisation as a whole (Indeed, 2023). To ensure alignment with organisational objectives, it is imperative to actively involve key stakeholders, subject matter experts, and the target audience in order to gather valuable insights and facilitate the development of content that is relevant to their needs and deficiencies within their roles
- Define Learning Objectives: The definition of learning objectives involves an explicit description of the intended learning outcomes and performance goals that the educational content should encompass as well as what the learners need to have attained at the end of the process (Indeed, 2023). It is imperative to establish objectives that possess the qualities of measurability, specificity, and relevance to the learners’ roles and responsibilities.
- Involve Instructional designers and Experts in key fields: One recommendation is to include instructional designers and experts in the development process (Hayden, 2022). Thus, the organisation needs to take an active role part in collaborative efforts with instructional designers or learning professionals who possess specialised knowledge in the creation of impactful digital learning materials. They have the ability to provide support in the development of educational material that adheres to the principles of learning, integrates interactive components, and makes effective use of suitable multimedia assets.
- Pilot and Testing Phase: Before the complete implementation, it is recommended to carry out pilot tests of the learning resources with a limited number of representative learners (Hayden, 2022). This way, organisations are able to collect feedback and evaluate its efficacy in achieving their learning needs and goals. It also avails a chance to make the required revisions in accordance with the feedback provided.
- Implement Continuous Evaluation and Improvement Plans: Organisations need to develop mechanisms that will allow them to consistently assess the influence of the content on learner engagement and performance (Indeed, 2023). The process involves monitoring feedback from learners and gathering data on completion rates, knowledge retention, and skill application. They can utilise this feedback to implement iterative enhancements and guarantee the content being provided provides continuous relevance and efficacy.
Organisations can optimise the influence of digital learning content on learner engagement and attain the intended learning outcomes by carefully considering these attributes and adhering to a methodical approach in content selection and development.
Task 2
Part A – Digital Facilitated Presentation
AC 2.3: Develop a digital facilitated presentation where engaging learning content is presented using a live online facilitation tool, demonstrating use of effective visual design
AC 3.4: Demonstrate online facilitation skills within a live online learning activity where interactive learner activities, such as questions, breakout rooms and polls are used to engage the learners with the content
Title: Legal Responsibility under the Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005
Introduction
- This presentation will discuss the legal responsibility of the Responsible Person under the Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005 (RRO).
- The RRO is the main piece of legislation that sets out the fire safety requirements for non-domestic premises in England and Wales.
- The RRO applies to all workplaces, regardless of size or industry.
- The Responsible Person is usually the employer, but it can also be the owner of the premises or another person who has control of the premises.
Overview of the Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005
- The RRO sets out several key requirements that the Responsible Person must meet, including:
- Carrying out a fire risk assessment
- Taking appropriate fire precautions
- Providing information and training
- The RRO also sets out a number of consequences for non-compliance, such as legal penalties, reputational damage, and increased risk to life and property.
Responsibilities of the Responsible Person
- The Responsible Person has several key responsibilities under the RRO, including:
- Ensuring the safety of employees and others who may be affected by fire in their workplace
- Carrying out a fire risk assessment
- Taking appropriate fire precautions
- Providing information and training
Risk Assessment
- A fire risk assessment is a systematic process of identifying and evaluating fire hazards in a workplace.
- The fire risk assessment should identify the potential causes of fire, the people who may be affected by fire, the precautions, and the likelihood and consequences of a fire occurring.
Fire Safety Measures
- Fire safety measures are the physical and procedural controls that are put in place to reduce the risk of fire and protect people from the effects of fire.
- Fire safety measures can include:
- Fire alarms
- Fire extinguishers
- Emergency escape routes
- Fire doors
- Fire blankets
- Fire wardens
- Fire drills
Fire Safety Training and Drills
- Fire safety training is essential for ensuring that employees know how to respond to a fire.
- Fire safety training should cover:
- The fire risk assessment
- The fire safety procedures
- How to use fire safety equipment
- What to do in the event of a fire
- Fire drills are a practical way of testing fire safety procedures and ensuring that employees know what to do in the event of a fire.
Record Keeping
- The Responsible Person must keep records related to fire safety, such as:
- Fire risk assessment reports
- Training records
- Maintenance records
- These records should be kept for a minimum of three years.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
- The consequences of non-compliance with the RRO can be serious, including:
- Legal penalties
- Reputational damage
- Increased risk to life and property
- The Responsible Person could be held personally liable for any loss or damage caused by a fire if they fail to comply with their legal obligations.
Conclusion
- The RRO is an important piece of legislation that sets out the fire safety requirements for workplaces in England and Wales.
- The Responsible Person has several key responsibilities under the RRO, including carrying out a fire risk assessment, taking appropriate fire precautions, and providing information and training.
Q&A Session
- What is the purpose of the Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005?
- What are the legal responsibilities of employers under the Fire Safety Order?
- What are the consequences of non-compliance with the Fire Safety Order?
Breakout Rooms Scenarios:
- Scenario Analysis: This will entail dividing learners into groups and providing them with different scenarios related to fire safety in various settings. Then I will ask them to discuss the legal responsibilities of the relevant parties involved and propose appropriate actions to ensure compliance with the Fire Safety Order.
Polls:
- True or False: The Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005 applies only to commercial buildings.
- Rate your organization’s current level of compliance with the Fire Safety Order on a scale of 1-5 (1 being non-compliant, 5 being fully compliant).
- What is the most challenging aspect of meeting legal responsibilities under the Fire Safety Order?
Part B – A written response to the following Assessment Criteria:
AC 3.1: Comparison of Online Delivery Methods for Live Online Learning Activities
- Cisco Webex:
Key Facilitation Functions:
- Video Conferencing: It provides high-quality video conferencing capabilities, allowing facilitators and learners to see and interact with each other in real-time.
- Screen Sharing: Facilitators can share their screens to present slides, documents, or multimedia content, enhancing visual engagement and collaboration.
- Chat and Q&A: It offers chat and Q&A features, enabling participants to ask questions, provide feedback, and engage in discussions during the session.
- Recording and Playback: Webex allows sessions to be recorded for future reference or for learners who couldn’t attend the live session (Panchal, 2023).
Strengths:
- It provides robust video and audio capabilities, ensuring clear communication during live sessions.
- The breakout rooms feature enables interactive group activities and discussions, fostering collaboration among learners.
- The recording feature allows learners to review the session content at their convenience (Panchal, 2023).
Weaknesses:
- Webex can be resource-intensive, requiring a stable internet connection for optimal performance.
- The user interface may be difficult to navigate for new participants (Panchal, 2023).
- Microsoft Teams:
Key Facilitation Functions:
- Video Meetings: it offers video meeting functionality, allowing interaction through video and audio communication.
- Chat and Collaboration: it has a chat feature for text-based communication, along with collaboration tools like document sharing and co-editing.
- Live Event Broadcasting: it can host live events allowing for larger-scale webinars or presentations with audience engagement features.
- Screen Sharing and Whiteboarding: it allows facilitators to share their screens and utilize virtual whiteboarding tools for visual presentations and collaboration (Khidir et al., 2022).
Strengths:
- Since it is a collaboration hub, it provides a familiar interface for users already using Microsoft tools.
- It allows for easy access to shared files and collaboration on documents.
- It supports larger-scale events and webinars with audience engagement features (Khidir et al., 2022).
Weaknesses:
- Limitations in terms of video quality compared to other video conferencing platforms.
- The chat-based feature may be unfavourable for highly interactive sessions.
- Some advanced features, may require additional licenses or configurations (Khidir et al., 2022).
AC 3.2: Differences in Facilitation of Live Online Learning vs. Face-to-Face Learning
- Facilitators:
- Technology Proficiency: Facilitators need to be proficient in using the online learning platform and associated tools to effectively deliver content and engage learners.
- Virtual Presence: Building rapport and establishing a connection with learners in an online environment requires different strategies than face-to-face interactions. Facilitators need to adapt their communication and facilitation techniques to create an engaging virtual presence.
- Managing Technology: Facilitators must handle technical issues that may arise during online sessions, such as audio or video problems, to ensure a smooth learning experience (Olmstead, 2022).
- Learners:
- Self-Directed Learning: Learners need to take more ownership of their learning in an online environment, managing their time, staying motivated, and actively participating in virtual activities..
- Technical Skills: Learners must be comfortable using the online learning platform, navigating through digital resources, and effectively participating in discussions and activities.
- Reduced Non-Verbal Cues: In a virtual setting, non-verbal cues may be limited, making it essential for learners to express themselves clearly through written communication and actively seek clarification when needed (Olmstead, 2022).
- Learning Administration:
- Logistics and Technical Support: Learning administration teams need to coordinate schedules, manage access to online platforms, and provide technical support to both facilitators and learners.
- Data Management: Online learning generates data and analytics that can be leveraged for learner tracking and performance evaluation.
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring the quality and consistency of online learning experiences requires monitoring sessions, collecting feedback, and making continuous improvements to the online delivery methods (Olmstead, 2022).
AC 3.3: Facilitation Skills for Live Online Learning and SMART Development Objective
Some of the key facilitation skills that are essential for effective live online learning:
- Communication and Engagement:
The successful facilitation of communication and engagement in a virtual setting necessitates the proficient delivery of ideas, instructions, and feedback by facilitators (Somji, 2022). To foster active participation and collaborative learning, it is imperative for educators to effectively involve learners through diverse communication channels.
- Proficiency in Technical Skills
Facilitators must possess an in-depth knowledge of the online learning platform and its corresponding tools (Somji, 2022). Proficiency in effectively managing audio/video settings, screen sharing capabilities, breakout room functionalities, and other essential features is imperative for delivering engaging sessions.
- Adaptability and flexibility
These qualities are crucial for facilitators, as they must be able to modify their facilitation styles to suit the online environment, which may necessitate the utilization of distinct approaches and techniques in contrast to traditional face-to-face settings (Somji, 2022).
SMART Development Objective
The objective of SMART development is to create specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound goals that facilitate progress and success in various areas of personal and professional growth.
Objective: To enhance my proficiency in communication and engagement within the context of live online learning. By the end of the academic quarter, I aim to engage in a facilitation training program that specifically concentrates on virtual communication and engagement techniques. Subsequently, I will implement a minimum of three new techniques acquired from this training during live online learning sessions, to augment learner participation and foster collaboration.
The stated objective demonstrates the characteristics of being SMART. It is specific as it focuses on enhancing communication and engagement skills. The objective is measurable as it involves participating in a training program and implementing three strategies. It is achievable within the quarter, making it realistic. The objective is relevant as it directly relates to the identified area of development. Lastly, it is time-bound, with a deadline set for completion by the end of the quarter.
To achieve this objective, I will take the following actions:
- I will research facilitation training programs that specifically focus on virtual communication and engagement techniques.
- I will enrol and actively participate in training sessions.
- After gaining knowledge and insights from the training program, I will actively apply at least three new communication and engagement strategies during live online learning sessions.
- I will reflect on the effectiveness of the implemented strategies and their impact on learner participation and collaboration. I will also seek feedback from learners and colleagues to gather insights on their experience and identify areas for improvement.
- I will make adjustments to the strategies and approaches used in future live online learning activities. I will continuously iterate and refine my communication and engagement techniques to optimize learner participation and collaboration.
References
FAO (2011) E-learning methodologies A guide for designing and developing e-learning courses. Available at: https://www.elearningnews.it/_resources/images/ebook/e-learning-methodologies.pdf.
Fedoruk, K. (2022) 5 Ideas to Use PDF In eLearning, eLearning Industry. Available at: https://elearningindustry.com/ideas-to-use-pdf-in-elearning.
Glenister, N. (2020) 9 Reasons To Use More Technologies In Learning And Development, eLearning Industry. Available at: https://elearningindustry.com/reasons-use-more-technologies-in-learning-and-development.
Hayden, D. (2022) Identifying learning & development needs: Factsheets, CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.org/en/knowledge/factsheets/learning-needs-factsheet/#How.
Indeed (2023) How to identify learning and development needs: A guide. Available at: https://uk.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/learning-and-development-needs.
Ivec, S. (2021) Why You Should be Using Scenarios in e-Learning, eLearning Industry. Available at: https://elearningindustry.com/why-you-should-be-using-scenarios-in-e-learning.
Khidir, M.L.B.M., Bin Sa’ari, S.N. and Bin Mohammad, A.S. (2022) ‘Effectiveness of online learning with Microsoft Team Applications in POLIMAS’, EPRA International Journal of Environmental Economics, Commerce and Educational Management, pp. 29–33. doi:10.36713/epra10260.
London Fire Brigade (2023) The Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005 – Fire Safety Law. Available at: https://www.london-fire.gov.uk/safety/the-workplace/fire-safety-law-explained/#:~:text=By%20law%2C%20if%20you%20are,licence%20under%20enactment%20in%20force.
Manning, K. (2021) Top 10 Challenges Faced by Learning and Development Professionals, ProcessMaker. Available at: https://www.processmaker.com/blog/top-10-challenges-faced-by-learning-and-development-professionals/.
Neelakandan, N. (2019) 7 different types of infographics to use in eLearning, Wizcabin. Available at: https://wizcabin.com/7-different-types-of-infographics-to-use-in-e-learning/.
Olmstead, L. (2022) Online Learning vs. Face-to-Face Learning: Which Is Best? The Whatfix Blog | Drive Digital Adoption. Available at: https://whatfix.com/blog/online-learning-vs-face-to-face-learning/#.
Panchal, R. (2023) 20+ Pros and Cons of Cisco Webex (Explained), List of Pros and Cons to make you a sensible decision. Available at: https://thenextfind.com/pros-cons-cisco-webex/.
Schorn, A. (2022) Online explainer videos: Features, benefits, and effects, Frontiers. Available at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcomm.2022.1034199/full.
Sethu, K. (2021) Top 6 Factors to Consider When Choosing a Technology Solution for your School, Orah. Available at: https://www.orah.com/blog/top-6-factors-to-consider-when-choosing-a-technology-solution-for-your-school.
Somji, R. (2022) Key facilitation skills for trainers and how to improve them, VirtualSpeech.
Available at: https://virtualspeech.com/blog/facilitation-skills-for-trainers
Get your 5OS02 Assignment Answers today By ordering your Copy, Speak to our experts today for all cipd Level 5 Assignment querries.
[vc_row full_width=”” parallax=”” parallax_image=””][vc_column width=”1/1″][vc_widget_sidebar sidebar_id=”default”][/vc_column][/vc_row]
